
Last Updated: 16 July 2023
Before we get into ISRO Quiz Questions And Answers, Do You know that ISRO is planning to carry out a Mission to the Sun?
Yes, You heard it right! The Indian Space Research Organisation is planning to send a Spacecraft “Aditya-L1” to study the sun.
The One and Only Space Agency of the Government of India, The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is located in Bangalore and was formed on 15 August 1969.
In this article, You’ll find many Important ISRO Quiz Questions and Answers that will help boost your knowledge and also for various Competitive Exams. Read this 100 Objective Questions & Answer and Improve your Exam Performance.
Page Contents
ISRO At A Glance
| No. | Header | Statements |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Vission | Harness space technology for national development, while pursuing space science research and planetary exploration |
| 2 | Mission | 1) Design and development of launch vehicles and related technologies for providing access to space. 2) Design and development of satellites and related technologies for earth observation, communication, navigation, meteorology, and space science. 3) Indian National Satellite (INSAT) programme for meeting telecommunication, television broadcasting, and developmental applications. 4) Indian Remote Sensing Satellite (IRS) programme for management of natural resources and monitoring of the environment using space-based imagery. 5) Space-based Applications for Societal development. 6) Research and Development in space science and planetary exploration. |
| 3 | Objectives | 1) Operational flights of Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV). 2) Developmental flight of Geo-synchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV- Mk II). 3) Development of heavy-lift Geo-synchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV-Mk III). 4) Design, Development, and Realization of Communication Satellites. 5) Design, Development, and Realization of Earth Observation Satellites. 6) Development of Navigation Satellite Systems. 7) Development of satellites for Space Science and Planetary Exploration. 8) Earth Observation Applications. 9) Space-based systems for Societal Applications. 10) Advanced Technologies and newer initiatives. 11) Training, Capacity Building, and Education. 12) Promotion of Space technology. 13) Infrastructure / Facility Development for space research. 14) International Cooperation. |
ISRO Quiz Questions And Answers
1. Where is the Headquarters of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)?
a) Pune
b) Bangalore
c) Lucknow
d) Mumbai
2. When was ISRO formed?
a) 15 August 1947
b) 15 August 1952
c) 15 August 1969
d) 15 August 1967
3. What is the Full Form of SDSC?
a) Satish Development Space Centre
b) Scientific Development Space Centre
c) Satish Dhawan Space Centre
d) Static Development Space Centre
4. Who is the Owner of the Indian Space Research Organisation?
a) Department of Space
b) Department of State
c) Distributed Operating Space
d) Dioctyl Sebacate
5. Which Satellite is responsible for Communication, Meteorological Services, and Television Broadcasting in India?
a) IRS
b) INSATTP
c) INPUT
d) INSAT
6. Which Satellite is used for Resources Monitoring and Management by ISRO?
a) IRIS
b) INSAT
c) IRS
d) ISS
7. What is the Full Form of PSLV?
a) Public Satellite Launch Vehicle
b) Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle
c) Polar Service Launch Vehicle
d) Public Service Launch Vehicle
8. When was the First Rocket launched from India?
a) 21 December 1963
b) 21 October 1963
c) 21 November 1964
d) 21 November 1963
9. What was ISRO known before 1969?
a) INCOSPAR
b) ACROSS
c) DAE
d) INSA
10. Where is the Indian Institute of Remote Sensing (IIRS)?
a) Hyderabad
b) Dehradun
c) Ahmedabad
d) Sriharikota
Related: 100+ Electric Car Companies With Car Models
11. What is the Full Form of GSLV?
a) Global Satellite Launch Vehicle
b) Geosynchronous Service Launch Vehicle
c) Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle
d) Geo Satellite Launch Vehicle
12. Who is the Father of the Indian Space Program?
a) C. V. Raman
b) Vikram Sarabhai
c) M. G. K. Menon
d) A. P. J. Abdul Kalam
13. A material is Dimensionally Stable at room temperature if its Glass Transition Temperature (Tg) is?
a) Below Room Temperature
b) Well Above Room Temperature
c) Just Above Temperature
d) Equal To Room Temperature
14. When was Chandrayaan-1 launched?
a) 22 October 2018
b) 22 October 2006
c) 22 October 2008
d) 22 October 2010
15. When was Chandrayaan-2 launched?
a) 22 July 2018
b) 22 July 2019
c) 22 July 2020
d) 22 July 2015
16. Where was Chandrayaan-2 launched?
a) ISRO Satellite Centre
b) Satish Dhawan Space Centre First LaunchPad
c) Satish Dhawan Space Centre Second LaunchPad
d) Laboratory for Electro-Optics Systems
17. Who was elected as the Chairman of the Indian Space Research Organisation on 15 January 2018?
a) Shailesh Nayak
b) K. Sivan
c) A. S. Kiran Kumar
d) K. Radhakrishnan
18. Name the First Satellite built by India?
a) Rohini RS-1
b) Aryabhata
c) Chandrayaan-1
d) SPADEX
19. Which Satellite made India the First Nation to Succeed on its Maiden Attempt to Mars?
a) Rohini
b) Aryabhatta
c) Mangalyaan
d) Chandrayaan-1
20. Who was the First Chairman of the Indian National Committee for Space Research (INCOSPAR)?
a) Vikram Sarabhai
b) M. G. K. Menon
c) Satish Dhawan
d) K. Sivan
Space Commission
| No. | Name | Post |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | S. Somanath | Chairman, ISRO Secretary, Department of Space |
| 2 | P. K. Mishra | Principal Secretary to PM |
| 3 | Ajit Doval | National Security Advisor to PM |
| 4 | Rajiv Gauba | Cabinet Secretary |
| 5 | Ajay Kumar Sood | Principal Scientific Adviser to GOI |
| 6 | Pawan Kumar Goenka | Chairman, IN-SPACe |
| 7 | Vinay Mohan Kwatra | Foreign Secretary |
| 8 | T.V. Somanathan | Expenditure Secretary |
| 9 | Anurag Jain | Secretary, DPIIT |
| 10 | K. Radhakrishnan | Chairman, Standing Committee IIT Council |
| 11 | A. S. Kiran Kumar | Vikram Sarabhai Professor |
| 12 | Talleen Kumar | Secretary to GOI |
| 13 | Goverdhan Mehta | National Research Professor |
| 14 | M. Maheshwar Rao | Joint Secretary & Financial Adviser, DOS |
| Last Updated: 16 July 2023 |
Related: 600+ ISRO Related Full Forms (2023 Updated)
21. Who is known as the Missile Man of India?
a) Satyendra Nath Bose
b) Vikram Sarabhai
c) C.V. Raman
d) A. P. J. Abdul Kalam
22. Which Missile was developed Under A. P. J. Abdul Kalam’s Guidance?
a) K15
b) MPATGM
c) Prithvi
d) Surya
23. Which is the First Successful Nuclear Bomb Test by India on 18 May 1974?
a) Pokhran-II
b) Smiling Buddha
c) Angry Bird
d) PTR
24. When was the Indian National Committee for Space Research (INCOSPAR) Set Up?
a) 1962
b) 1965
c) 1947
d) 1947
25. What is the Name of the Indian Space University?
a) Physical Research Laboratory (PRL)
b) Indian Institute of Science (IISc)
c) Indian Institute of Remote Sensing (IIRS)
d) Indian Institute of Space Science & Technology (IIST)
26. Where is Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre?
a) Ahmedabad
b) Chandigarh
c) Thiruvananthapuram
d) Mohali
27. Which Satellite is used by Tata Sky?
a) CartoSat-1
b) INSAT-4CR
c) INSAT-99
d) INSAT-4A
28. Which Series of Indian Satellites are Decommissioned?
a) ASLV
b) PSLV
c) GSLV
d) GSLV Mk III
29. How many Polar Satellite Launch Vehicles (PSLV) failed during the 1990s?
a) 4
b) 3
c) 0
d) 1
30. When did Mangalyaan-1 Enter the Mars orbit?
a) 24 September 2019
b) 24 September 2014
c) 24 September 2008
d) 24 September 2018
Missions by ISRO
| No. | Label | Missions |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Spacecraft Missions (including 3 Nano Satellites, 1 Micro Satellite) | 124 |
| 2 | Launch Missions (Including Scramjet-TD, RLV-TD, and Crew Escape System) | 92 |
| 3 | Student Satellites | 15 |
| 4 | Re-entry Missions | 2 |
| 5 | Foreign Satellites (out of 34 Countries) | 424 |
| 6 | Satellites Realised by Indian Private Players | 3 |
| Last Updated: 17 Jul 2023 |
Related: Time And Distance Multiple Choice Questions (Boost Your IQ)
31. Which is the Twenty-Third Geostationary Communication Satellite of India that is intended to Extend C and Ku-Band Transponders?
a) GSAT-3
b) GSAT-D5
c) GSAT-15
d) GSAT-14
32. How many Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicles (GSLVs) failed during the 2010s?
a) 1
b) 3
c) 2
d) 0
33. Which type of Indian Satellites did Not Fail even once?
a) PSLV
b) GSLV Mk III
c) GSLV Mk V
d) GSLV Mk VI
34. Which Satellite is used by Doordarshan for providing Television Services all over India?
a) GSAT
b) INSAT
c) IRNSS
d) Cartosat
35. How many Radar Imaging Satellites (RISAT) does ISRO currently Operate?
a) Two
b) One
c) Four
d) Three
36. Which was the first Satellite of the RISAT series to reach Orbit?
a) RISAT-2B
b) RISAT-3
c) RISAT-2
d) RISAT-1
37. Which was the first dedicated Meteorological Satellite launched by ISRO using the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle on 12 September 2002?
a) Kalpana-1
b) Aryabhatta-1
c) Kalpana-2
d) Aryabhatta-2
38. Who renamed MetSat-1 to Kalpana-1 on 1st February 2003?
a) A. P. J. Abdul Kalam
b) Atal Bihari Vajpayee
c) Narendra Modi
d) Jawaharlal Nehru
39. Which is the First Navigation Satellite of India?
a) IRNSS-3A
b) IRNSS-2A
c) IRNSS-1A
d) IRNSS-7A
40. How many Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System was launched to complete India’s own Navigation System?
a) 7
b) 4
c) 5
d) 2
Related: List Of Top 50 FMCG Companies In India With Their Brands
41. Out of the 7 Active Indian Regional Navigation Satellite Systems, How many are in Geostationary Orbit (GEO) and Inclined Geosynchronous Orbit (IGSO)?
a) 4 GEO, 3 IGSO
b) 3 GEO, 4 IGSO
c) 2 GEO, 5 IGSO
d) 5 GEO, 2 IGSO
42. Which Spacecraft was Mentioned by Prime Minister Narendra Modi on 15 August 2018 that will send Astronauts into Space?
a) Astrosat
b) Chandrayaan-V
c) Gaganyaan
d) Pragyan
43. What was the Mission of Chandrayaan-1?
a) Satellite Navigation and GPS
b) Remote Sensing and Planetary Science
c) Observation Satellite
d) Atmospheric and Space sciences
44. Who was the Project Director of Chandrayaan-1?
a) Shailesh Nayak
b) R. Hutton
c) K. Sivan
d) M. Annadurai
45. When was the Department of Space (DoS) established?
a) 1971
b) 1972
c) 1947
d) 1999
46. Which are the Two Satellite Launch Vehicles developed by ISRO?
a) IRS and PSLV
b) INSAT and IRS
c) PSLV and GSLV
d) GSLV and IRS
47. Where are Indian Satellites Manufactured?
a) Laboratory for Electro-Optics Systems (LEOS)
b) Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC)
c) Space Applications Centre (SAC)
d) ISRO Satellite Centre (ISAC)
48. How many Scientific Instruments did Chandrayaan-1 carry onboard?
a) 11
b) 12
c) 10
d) 5
49. Where was Chandrayaan-1 Launched?
a) Ahmedabad
b) Gadanki
c) Sriharikota
d) Umiam
50. Which is the First Indian Multi-Wavelength Space Telescope?
a) XPoSat
b) Astrosat
c) GSLV Mk III
d) XL-C33
Extraterrestrial Probes
| No. | Destination | Craft name | Launch vehicle | Planned |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Sun | Aditya-L1 | PSLV-XL | 2024 |
| 2 | Moon | Chandrayaan-3 | GSLV Mk III | Done |
| 3 | Venus | Shukrayaan-1 | GSLV Mk II | 2024 |
| 4 | Mars | Mars Orbiter Mission 2 (Mangalyaan 2) | GSLV Mk III | 2024 |
Related: List Of All Social Networking Sites And Their Founders
51. What was U R Rao Satellite Centre (URSC) formerly known?
a) Master Control Facility (MCF)
b) ISRO Satellite Centre (ISAC)
c) Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre (LPSC)
d) New Space India Limited (NSIL)
52. When did U R Rao Satellite Centre (URSC) launch its 100th Satellite?
a) 12th January 2018
b) 12th January 2019
c) 12th January 2020
d) 12th January 2017
53. Where are the Rockets and Launch Vehicles made in India?
a) Space Applications Centre (SAC)
b) Master Control Facility (MCF)
c) Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC)
d) Semi-Conductor Laboratory (SCL)
54. From where are the Sounding Rockets launched in India?
a) ISRO Satellite Centre
b) Thumba Equatorial Rocket Launching Station
c) National Remote Sensing Centre
d) Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre
55. What is “RH” on an Indian Sounding Rocket?
a) Rhodium
b) Relative Humidity
c) Rohini
d) Red Hat
56. Which Rocket was launched on 21st November 1963 in India?
a) Scramjet
b) Nike Apache
c) Bahubali
d) XUV
57. Which is the First Indigenous Sounding Rocket launched in India?
a) RH-125
b) RH-100
c) RH-95
d) RH-75
58. Where did the Space Program begin in India?
a) National Remote Sensing Centre
b) Thumba Equatorial Rocket Launching Station
c) ISRO Satellite Centre
d) Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre
59. Why was Thumba Rocket Station selected as a Rocket Launching Station?
a) The Equator
b) Geomagnetic Equator
c) Tropic of Cancer
d) Tropic of Capricon
60. Which Rockets are known as Research Rockets?
a) Solid-Fuel Rocket
b) Liquid-Fuel Rocket
c) Plasma Rocket
d) Sounding Rocket
Spacecraft Launchers by ISRO
| No. | Launchers | Height | Lift-off Weight | Propulsion | Payload Mass | Orbit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SLV-3 | 22.7 m | 17 t | All Solid | 40 Kg | Low Earth Orbit |
| 2 | ASLV | 23.5 m | 39 t | All Solid | 150 Kg | Low Earth Orbit |
| 3 | PSLV-XL | 44 m | 320 t | Solid & Liquid | 1860 Kg | Sun-Synchronous Polar Orbit |
| 4 | GSLV MK II | 49 m | 414 t | Solid, Liquid, & Cryogenic | 2200 Kg | Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit |
| 5 | GSLC MK III | 43.43 m | 640 t | Solid, Liquid, & Cryogenic | 4000 Kg | Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit |

Related: 100 Facts About Elon Musk You Never Heard: Wife, Career, Net Worth, etc
61. Which Space Centre was renamed after Dr. Vikram Sarabhai?
a) Sarabhai Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC)
b) Sarabhai Space Centre (SSC)
c) Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC)
d) Vikram Sensing Space Centre (VSSC)
62. How many Centres of ISRO are in Bengaluru?
a) 12
b) 13
c) 15
d) 21
63. Which is the only Indian Island where ISRO has Set up a Space Centre?
a) Diu Island
b) Andaman
c) Port Blair
d) Great Nicobar
64. Where is the National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC)?
a) Ahmedabad
b) Sriharikota
c) Hyderabad
d) Thiruvananthapuram
65. Which is the First Launch Vehicle of India?
a) SLV-2
b) SLV-3
c) SLV-1
d) SLV-99
66. Where are Communication Satellites Placed?
a) Low Earth Orbit
b) Medium Earth Orbit
c) Polar Orbit
d) Geostationary Orbit
67. Where are Remote Sensing Satellites Placed?
a) Low Earth Orbit
b) Sun-Synchronous Polar Orbit
c) Geostationary Transfer Orbit
d) Lagrange Points
68. Where was the First Indian Satellite “Aryabhata” launched?
a) United States
b) Russia
c) Soviet Union
d) India
69. Which is the First Operational Launch Vehicle of India?
a) ASLV
b) PSLV
c) SLV-3
d) GSLV
70. What does Yaan mean in “Chandrayaan”?
a) Rocket
b) Moon
c) Vehicle
d) Space
Related: MCQ Questions On Volume And Surface Area Of Solids
71. How many Days was Chandrayaan-1 Operational?
a) 365 Days
b) 312 Days
c) 730 Days
d) 291 Days
72. How many Scientific Instruments were from NASA on Chandrayaan-1?
a) 2
b) 3
c) 1
d) 6
73. What is the Temperature of the Moon at Night?
a) -967 ºC
b) -173 ºC
c) 173 ºC
d) 68 ºC
74. Which is the Heaviest Satellite built by India?
a) INSAT-4CR
b) INSAT-4DR
c) GSAT-11
d) GSAT-30
75. Which Mission is related to Mangalyaan?
a) MarCO
b) Phoenix
c) Mars Orbiter Mission
d) Mars Express
76. In which Year will Mangalyaan-2 be launched by ISRO?
a) 2034
b) 2029
c) 2023
d) 2024
77. Who is One of the Responsible Persons for the Department of Space (DoS)?
a) The President of India
b) The Prime Minister of India
c) Minister of Technical
d) The Vice President of India
78. Which Mission was Launched by ISRO using a Modified Version of the PSLV on 22 October 2008?
a) Mangalyaan-1
b) Mangalyaan-2
c) Chandrayaan-1
d) Chandrayaan-2
79. Which is the First Country to enter Mars orbit on its first attempt?
a) USA
b) Russia
c) India
d) Kazakhstan
80. Which Spacecraft is Developed by ISRO to study the Sun?
a) Shukrayaan-1
b) Aditya-L1
c) Aditya-L2
d) Mangalyaan-3
Operational Sounding Rockets
| No. | Vehicle | Payload (Kg) | Altitude (Km) | Purpose | Launch Pad |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | RH-200 | 10 | 80 | Meteorology | Thumba Balasore |
| 2 | RH-300-Mk-II | 60 | 160 | Aeronomy | SDSC-SHAR |
| 3 | RH-560-MK-II | 100 | 470 | Aeronomy | SDSC-SHAR |
Related: List of Top Websites On the Internet And Their Founders
81. Which Space Technology Incubation Centre is serving the East Region?
a) National Institute of Technology, Silchar
b) National Institute of Technology, Meghalaya
c) National Institute of Technology, Mizoram
d) National Institute of Technology, Agartala
82. Who promotes Products, Services, and Technology developed by ISRO?
a) HRD
b) Antrix
c) NSIL
d) SLV
83. Which Spacecraft is Developed by ISRO for a Mission to Venus?
a) Venusayaan-1
b) Venusian
c) Shukrayaan-1
d) TBD
84. Which Satellite is used by the Indian Military as a Communication Satellite?
a) Sat-1
b) GSAT-7A
c) SCAT
d) IRNSS-1H
85. What is the Full Form of “SITE” that was used for Conducting Large Scale Video Broadcasting?
a) System Instructional Television Experiment
b) Signal Integrity Television Experiment
c) Sinhalese Instructional Television Experiment
d) Satellite Instructional Television Experiment
86. What is the Full Form of “APPLE”, which was an Experimental Communication Satellite launched by the ISRO on 19th June 1981?
a) Apple PugetSound Program Library Exchange
b) Ariane Passenger PayLoad Experiment
c) Ariane Passenger Program Load Experiment
d) Ariane Passenger PayLoad Exchange
87. What is the Total Number of Foreign Satellites launched by ISRO as of 4 December 2019?
a) 319
b) 699
c) 900
d) 569
88. How many Stages are there in Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle?
a) 2
b) 3
c) 5
d) 1
89. Which is the latest PSLV launched by ISRO?
a) PSLV-C44
b) PSLV-C46
c) PSLV-C48
d) PSLV-C42
90. When was the first Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) launched?
a) 2018
b) 1993
c) 1997
d) 2004
Related: List Of Top Richest Person In The World 2023 Updated
91. Where is Thumba Equatorial Rocket Launching Station situated?
a) Port Blair
b) Andhra Pradesh
c) Kerala
d) Tamil Nadu
92. Which fuel is used in the Second Stage of GSLV GS2?
a) LOX+LH2
b) N2O4+UDMH
c) HTPB
d) N2O4+LH2
93. Which is the First Satellite Exclusively used for Educational Sector?
a) GSAT-69
b) GSAT-5
c) GSAT-2
d) GSAT-3
94. Which is the First Indian Remote Sensing Satellite?
a) IRS-1A
b) IRS-2A
c) IRS-4A
d) IRS-3A
95. Who established the Indian National Committee for Space Research (INCOSPAR)?
a) C.V. Raman
b) Jawaharlal Nehru
c) Meghnad Saha
d) Vikram Sarabhai
96. Name the Indian Operation where an Anti-Satellite Weapon was Tested that made India the 4th country after the US, Russia, & China?
a) Mission Gaganyaan
b) Mission D6
c) Mission Shakti
d) Mission Tiger
97. When was the ISRO logo adopted?
a) 2001
b) 2002
c) 2005
d) 2009
98. Who was the First Indian to go to Space?
a) Ravish Malhotra
b) Kalpana Chawla
c) Rakesh Sharma
d) Rakesh Malhotra
99. Which is the First Indian Cartography Satellite?
a) SHAR
b) CARTOSAT-1
c) ArcGIS Pro
d) Cartosat-2B
100. Which is the First Indian Communication Satellite?
a) Aryabhatta
b) BhaskaraSega-I
c) APPLE
d) Rohini RS-1
Read The Latest 2023 Current Affairs of India and The World
101. When was PSLV-C53/DS-EO Mission launched?
a) 30 July 2022
b) 30 June 2022
c) 30 May 2022
d) 30 April 2022
102. From which space centre was the PSLV-C53/DS-EO Mission launched?
a) Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre
b) Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre
c) Satish Dhawan Space Centre
d) U R Rao Satellite Centre
103. When did the launch of the PSLV-C53/DS-EO Mission launch begin?
a) 24:00 hours
b) 21:00 hours
c) 19:00 hours
d) 17:00 hours
104. PSLV-C53/DS-EO is designed to orbit the DS-EO satellites along with two other co-passenger satellites from _______?
a) Singapore
b) United States
c) Russia
d) Spain
105. When did India’s Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle PSLV-C52 inject Earth Observation Satellite EOS-04, into an intended sun-synchronous polar orbit of 529 km altitude at 06:17 hours IST?
a) 14 February 2022
b) 14 March 2022
c) 14 April 2022
d) 14 May 2022
106. From which space center was the PSLV-C52 satellite launched?
a) U R Rao Satellite Centre
b) Space Applications Centre
c) Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre
d) Satish Dhawan Space Centre
107. Who is the new chairman of ISRO? (2023)
a) K. Sivan
b) S. Somanath
c) A. S. Kiran Kumar
d) K. Kasturirangan
108. Which Indian state has the highest number of Space Centres?
a) Karnataka
b) Gujarat
c) Maharashtra
d) Tamil Nadu
109. When was Indian National Committee for Space Research (INCOSPAR) established?
a) 1952
b) 1962
c) 1972
d) 1982
110. Where is the Headquarters of NewSpace India Limited (NSIL) located?
a) Karnataka
b) Andhra Pradesh
c) Puducherry
d) Andaman and Nicobar Islands
List Of Chairman Of ISRO
| No. | Chairman | Term In | Term Out | Total Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Vikram Sarabhai (1919–1971) | 1963 | 1971 | 8 Years |
| 2 | M. G. K. Menon (1928–2016) | Jan 1972 | Sep 1972 | 9 Months |
| 3 | Satish Dhawan (1920–2002) | 1972 | 1984 | 12 Years |
| 4 | U. R. Rao (1932–2017) | 1984 | 1994 | 10 Years |
| 5 | K. Kasturirangan (born 1940) | 1994 | 27 Aug 2003 | 9 Years |
| 6 | G. Madhavan Nair (born 1943) | Sep 2003 | 29 Oct 2009 | 6 Years |
| 7 | K. Radhakrishnan (born 1949) | 30 Oct 2009 | 31 Dec 2014 | 5 Years 62 Days |
| ~ | Shailesh Nayak (born 1953) | 1 Jan 2015 | 12 Jan 2015 | 11 Days |
| 8 | A. S. Kiran Kumar (born 1952) | 14 Jan 2015 | 14 Jan 2018 | 3 Years |
| 9 | K. Sivan (born 1957) | 15 Jan 2018 | 15 Jan 2022 | 4 Years |
| 10 | S. Somanath (born 1963) | 15 Jan 2022 | Incumbent | ~ |
111. AstroSat Mission is dedicated to Indian _______ Mission?
a) Astronomy
b) Mars Orbiter
c) Suborbital
d) Polar Satellite
112. How many ISRO centres are in India?
a) 10
b) 12
c) 14
d) 16
ISRO Space Centres
| No. | Centre | Acronym | Address | State |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre | VSSC | Trivandrum | Kerala |
| 2 | Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre | LPSC | Valiamala | Kerala |
| 3 | Satish Dhawan Space Centre | SDSC | Nellore | Andhra Pradesh |
| 4 | U R Rao Satellite Centre | URSC | Vimanapura | Karnataka |
| 5 | Space Applications Centre | SAC | Ahmedabad | Gujarat |
| 6 | National Remote Sensing Centre | NRSC | Hyderabad | Telangana |
| 7 | Human Space Flight Centre | HSFC | Bengaluru | Karnataka |
| 8 | ISRO Propulsion Complex | IPRC | Mahendragiri | Tamil Nadu |
| 9 | ISRO Inertial Systems Unit | IISU | Vattiyoorkavu | Kerala |
| 10 | ISRO Telemetry, Tracking, and Command Network | ISTRAC | Bengaluru | Karnataka |
| 11 | Master Control Facility | MCF | Hassan | Karnataka |
| 12 | Development and Educational Communication Unit | DECU | Ahmedabad | Gujarat |
| 13 | Laboratory for Electro-Optics Systems | LEOS | Bengaluru | Karnataka |
| 14 | Indian Institute of Remote Sensing | IIRS | Dehra Dun | Uttarakhand |
113. Where is the headquarters of Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC)?
a) Karnataka
b) Kerala
c) Andhra Pradesh
d) Tami Nadu
114. How many Autonomous Bodies are in the Department of Space of ISRO?
a) 2 Autonomous Bodies
b) 3 Autonomous Bodies
c) 4 Autonomous Bodies
d) 5 Autonomous Bodies
115. How many Central Public Sector Enterprises (CPSEs) are in the Department of Space?
a) One
b) Two
c) Three
d) Four
116. Under whose leadership was Indian National Committee for Space Research (INCOSPAR) set up?
a) Dr. Homi J. Bhabha
b) Udupi Ramachandra Rao
c) K. Radhakrishnan
d) A. S. Kiran Kumar
117. When was INCOSPAR set up?
a) 1952
b) 1962
c) 1972
d) 1982
118. Where is the headquarters of the Department of Space (DOS)?
a) Bangalore
b) Delhi
c) Chennai
d) Thiruvananthapuram
119. When was the Department of Space (DOS) established?
a) 1962
b) 1972
c) 1982
d) 1992
120. How many types of spacecraft are made by ISRO?
a) 4 Types
b) 7 Types
c) 9 Types
d) 11 Types
Types of Indian Spacecraft
| No. | Spacecraft | First Satellite | Launch Date | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Communication Satellites | INSAT-1A | 10 Apr 1982 | Fail |
| 2 | Earth Observation Satellites | Bhaskara-I | 07 Jun 1979 | Successful |
| 3 | Scientific Spacecraft | SROSS-1 | 24 Mar 1987 | Fail |
| 4 | Navigation Satellites | IRNSS-1A | 01 Jul 2013 | Successful |
| 5 | Experimental Satellites | Aryabhata | 19 Apr 1975 | Successful |
| 6 | Small Satellites | YOUTHSAT | 20 Apr 2011 | Successful |
| 7 | Student Satellites | ANUSAT | 20 Apr 2009 | Successful |
121. Which satellite was the first Earth Observation ( Experimental) satellite launched by ISRO?
a) Bhaskara-I
b) Rohini Satellite RS-D1
c) IRS-1A
d) SROSS-2
122. Which satellite was the first Navigation satellite launched by ISRO?
a) IRNSS-1A
b) IRNSS-1B
c) IRNSS-1C
d) IRNSS-1D
123. Name the first Experimental satellite launched by ISRO?
a) YOUTHSAT
b) Rohini Satellite RS-1
c) Rohini Technology Payload (RTP)
d) Aryabhata
124. How many types of Small Satellites had been configured and developed by ISRO?
a) One
b) Two
c) Three
d) Four
125. Name the first Small satellite launched by ISRO?
a) Microsat
b) YOUTHSAT
c) CARTOSAT
d) Rohini Technology Payload (RTP)
126. Who was the first Chairman of ISRO?
a) Dr. K. Radhakrishnan
b) Dr. Vikram Ambalal Sarabhai
c) Dr. Krishnaswamy Kasturirangan
d) Prof. M G K Menon
127. The main office of the early stages of India’s Space Programme was a _____?
a) Church
b) Beach
c) Fishing Spot
d) Jute Factory
128. How many operational launchers does ISRO have?
a) One
b) Two
c) Three
d) Four
129. Which is the heaviest launcher made by ISRO?
a) GSLV MK I
b) GSLV MK II
c) GSLV MK III
d) GSLV MK IV
130. Which is the tallest launcher made by ISRO?
a) ASLV
b) PSLV- XL
c) GSLV MK II
d) GSLV MK III
131. When was the first flight of the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) done?
a) 1993
b) 1994
c) 1995
d) 1996
132. How many Applications is ISRO working on to date?
a) Three
b) Five
c) Seven
d) Nine
133. When was Chandrayaan 2 approved by then Prime Minister Manmohan Singh?
a) 18th September 2006
b) 18th September 2007
c) 18th September 2008
d) 18th September 2009
134. When was SSLV-D1/EOS-02 launched?
a) 7th June 2022
b) 7th July 2022
c) 7th August 2022
d) 7th September 2022
135. At which space center was SSLV-D1/EOS-02 launched?
a) Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre
b) Satish Dhawan Space Centre
c) U R Rao Satellite Centre
d) Human Space Flight Centre
136. On what basis has ISRO developed the Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV) to cater to the launch of satellites to Low Earth Orbits?
a) Launch-On-Requirement
b) Launch-On-Request
c) Launch-On-Demand
d) Launch-On-Order
137. What was the weight of the EOS-02 satellite launched for the SSLV-D1 Mission?
a) 135 Kg
b) 145 Kg
c) 155 Kg
d) 165 Kg
138. What was the name of the other satellite launched in the SSLV-D1/EOS-02 Mission?
a) AmritSAT Satellite
b) FreedomSAT Satellite
c) MahotsavSAT Satellite
d) AzaadiSAT Satellite
139. How much weight can the Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV) cater to launch to Low Earth Orbits?
a) 500 Kg
b) 1000 Kg
c) 1500 Kg
d) 2000 Kg
140. EOS-02 is an __________ satellite designed and released by ISRO.
a) Navigation
b) Earth Observation
c) Communication
d) Scientific Spacecraft
141. ________ students from rural regions across the country were guided to build payloads for AzaadiSAT Satellite?
a) Only Girl
b) Only Boy
c) Both Boys & Girls
d) Girls and Lady Teachers
142. The payloads of the AzaadiSAT Satellite were integrated by the student team namely?
a) Planet Kidz
b) Space Kidz India
c) Exploring Kidz India
d) Kids Space
143. Which Transponder was to enable voice and data transmission in the AzaadiSAT satellite?
a) DRT
b) UHF-VHF
c) SAS & R
d) CDMA
144. 1 TECU =?
a) 1016 m-2
b) 1026 m-2
c) 1036 m-2
d) 1046 m-2
145. How many satellites were placed in the LVM3 M2/OneWeb India-1 Mission?
a) 34 Satellites
b) 35 Satellites
c) 36 Satellites
d) 37 Satellites
146. In which Space Centre was the LVM3 M2 launched?
a) Satish Dhawan Space Centre
b) Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre
c) Human Space Flight Centre
d) ISRO Propulsion Complex
147. When was the OneWeb India-1 Mission launched?
a) 21st October 2022
b) 22nd October 2022
c) 23rd October 2022
d) 24th October 2022
148. In the OneWeb India-1 Mission, it was the ______ flight of LVM3.
a) Fourth
b) Fifth
c) Sixth
d) Seventh
149. At what time LVM3 M2 was launched from the space centre?
a) 07:00 Hrs
b) 08:00 Hrs
c) 09:00 Hrs
d) 10:00 Hrs
150. Where is the Integrated Cryogenic Engine Manufacturing Facility (ICMF) located?
a) Bengaluru
b) Pune
c) New Delhi
d) Visakhapatnam
151. Which President of India inaugurated the Integrated Cryogenic Engine Manufacturing Facility (ICMF)?
a) Pratibha Patil
b) Pranab Mukherjee
c) Ram Nath Kovind
d) Draupadi Murmu
152. Who has been designated as the Principal Scientist of the Aditya-L1 Mission?
a) Dr. Sankarasubramanian K.
b) S. Somanath
c) Ajit Doval
d) Dr. P K Mishra
153. When was Vikram-Suborbital (VKS) Rocket launched?
a) 12 November 2022
b) 14 November 2022
c) 16 November 2022
d) 18 November 2022
154. Which is the first Indian Private Rocket to be launched into space?
a) INSAT-1B
b) Vikram-Suborbital
c) Oceansat-3
d) JITSat
155. Which company is the launch agency for Vikram-suborbital (VKS) rocket?
a) McDonnell-Douglas
b) Larsen & Toubro
c) Skyroot Aerospace
d) Arianespace SA
156. From which space centre was Vikram-Suborbital (VKS) Rocket launched?
a) Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre
b) Satish Dhawan Space Centre
c) Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre
d) Human Space Flight Centre
157. Which rocket marks the first launch of a launch vehicle built by a private company in India?
a) Vikram-S
b) GSAT-24
c) INSAT 3DS
d) AstroSat-2
158. How many payloads did the Vikram-Suborbital (VKS) rocket carry?
a) One
b) Two
c) Three
d) Four
159. What is the name of the mission in which the Vikram–Suborbital (VKS) rocket was launched?
a) Mission Prarambh
b) Mission ASTROSAT
c) Mission Aditya
d) Mission Shukrayaan
160. Where was the Integrated Main Parachute Airdrop Test (IMAT) performed on 18 November 2022?
a) Uttarakhand
b) Uttar Pradesh
c) Andhra Pradesh
d) Kerala
161. Where is the headquarters of Bellatrix Aerospace?
a) Visakhapatnam
b) Hyderabad
c) Pune
d) Bangalore
162. Where is the first private launchpad & mission control centre established on the ISRO campus?
a) LPSC
b) VSSC
c) SDSC
d) URSC
163. Which President of India witnessed the 200th successive successful launch of RH200?
a) Draupadi Murmu
b) Ram Nath Kovind
c) Pranab Mukherjee
d) A. P. J. Abdul Kalam
164. Indian Space Research Organisation signed an MoU with Social Alpha to launch?
a) SpaceTech Innovation Network (SpIN)
b) Trisonic Wind Tunnel (TWT)
c) Flight Termination System (FTS)
d) Multi Object Tracking Radar (MOTR)
165. Where was the CE-20 Engine Hot Tested on 23rd December 2022?
a) Space Applications Centre
b) ISRO Propulsion Complex
c) Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre
d) Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre
166. When was LVM3-M3 launched?
a) 26 Jan 2023
b) 26 Feb 2023
c) 26 Mar 2023
d) 26 Apr 2023
167. What is the Mission name of the LVM3-M3 Vehicle?
a) OneWeb India-1 Mission
b) OneWeb India-2 Mission
c) OneWeb India-3 Mission
d) OneWeb India-4 Mission
168. Where was the LVM3-M3 Vehicle launched?
a) Satish Dhawan Space Centre
b) U R Rao Satellite Centre
c) Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre
d) ISRO Propulsion Complex
169. LVM3-M3 is the _______ consecutive successful flight of LVM3?
a) 4th
b) 5th
c) 6th
d) 7th
170. What is the payload of the LVM3-M3 Vehicle?
a) 4805 Kg
b) 5805 Kg
c) 6805 Kg
d) 7805 Kg
171. How many satellites did the LVM3-M3 place in their intended 450 km circular orbit with an inclination of 87.4 degrees?
a) 16 Satellites
b) 26 Satellites
c) 36 Satellites
d) 46 Satellites
172. When was PSLV-C55/TeLEOS-2 launched?
a) 22 Jan 2023
b) 22 Feb 2023
c) 22 Mar 2023
d) 22 April 2023
173. Where was PSLV-C55/TeLEOS-2 launched?
a) LPSC
b) SDSC
c) VSSC
d) URSC
174. The TeLEOS-2 satellite is developed under a partnership between ____ and ST Engineering?
a) DSTA
b) DSSA
c) DTSA
d) DATS
175. When was Chandrayaan-3 launched?
a) 10th July 2023
b) 12th July 2023
c) 14th July 2023
d) 16th July 2023
176. From which space centre was Chandrayaan-3 launched?
a) Space Applications Centre (SAC)
b) National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC)
c) Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC) SHAR
d) ISRO Telemetry, Tracking and Command Network (ISTRAC)
177. How many mission phases does Chandrayaan-3 have?
a) 8 Phases
b) 10 Phases
c) 12 Phases
d) 14 Phases
178. What is the mission life of Chandrayaan-3?
a) 2 to 4 months
b) 3 to 6 months
c) 4 to 8 months
d) 6 to 10 months
179. In which Launch vehicle was Chandrayaan-3 launched?
a) LVM3-M1
b) LVM3-M2
c) LVM3-M3
d) LVM3-M4
180. LVM3 aims to launch the Chandrayaan-3 spacecraft to _____?
a) Low Earth Orbit (LEO)
b) Geo Transfer Orbit (GTO)
c) Geostationary Orbit (GEO)
d) Medium Earth Orbit (MEO)
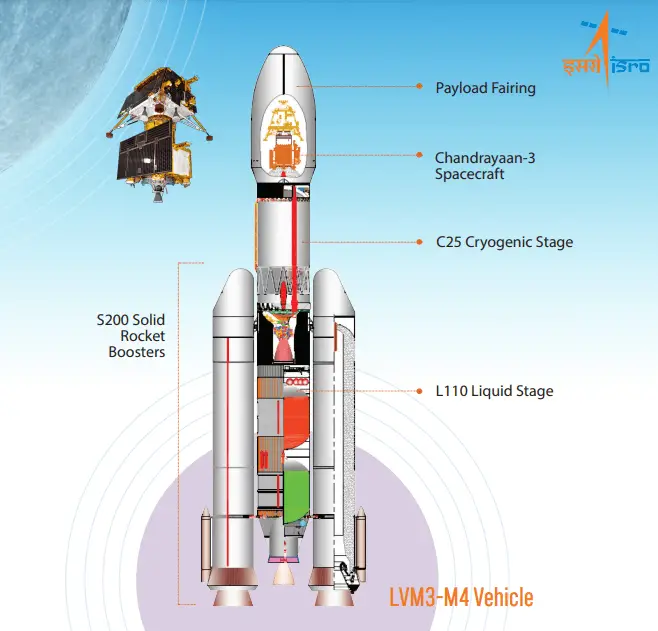
Chandrayaan-3 At A Glance
| 1 | Lander Payloads | 1) RAMBHA-LP: Langmuir Probe 2) ChaSTE: Chandra’s Surface Thermophysical Experiment 3) ILSA: Instrument for Lunar Seismic Activity |
| 2 | Rover Payloads | 1) APXS: Alpha Particle X-Ray Spectrometer 2) LIBS: Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscope |
| 3 | Propulsion Module Payload | SHAPE: Spectro-polarimetry of HAbitable Planet Earth |
| 4 | Objectives of Chandrayaan-3 | 1) To demonstrate Safe and Soft Landing on Lunar Surface 2) To demonstrate Rover roving on the moon and 3) To conduct in-situ scientific experiments. |
| 5 | Mass | 1) Propulsion Module: 2148 kg 2) Lander Module: 1752 kg including Rover of 26 kg 3) Total: 3900 kg |
| 6 | Power Generation | 1) Propulsion Module: 758 W 2) Lander Module: 738W, WS with Bias 3) Rover: 50W |
ISRO Related Full-Forms
| No. | Acronym | Full-Form |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | BFFR | Babina Field Fire Range |
| 2 | ChaSTE | Chandra’s Surface Thermophysical Experiment |
| 3 | DECU | Development and Educational Communication Unit |
| 4 | DOS | Department of Space |
| 5 | IAA | International Academy of Astronautics |
| 6 | IDSN | Indian Deep Space Network |
| 7 | IIRS | Indian Institute of Remote Sensing |
| 8 | IISU | ISRO Inertial Systems Unit |
| 9 | ILSA | Instrument for Lunar Seismic Activity |
| 10 | IMAT | Integrated Main Parachute Airdrop Test |
| 11 | INCOSPAR | Indian National Committee for Space Research |
| 12 | INSAT | Indian National Satellite |
| 13 | IPRC | ISRO Propulsion Complex |
| 14 | IRS | Indian Remote Sensing |
| 15 | ISTRAC | ISRO Telemetry, Tracking, and Command Network |
| 16 | LEOS | Laboratory for Electro-Optics Systems |
| 17 | LPSC | Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre |
| 18 | MCF | Master Control Facility |
| 19 | MOM | Mars Orbiter Mission |
| 20 | MPKs | Microprocessor-Controlled Knees |
| 21 | NARL | National Atmospheric Research Laboratory |
| 22 | NE-SAC | North Eastern Space Applications Centre |
| 23 | NNRMS | National Natural Resources Management System |
| 24 | NRSC | National Remote Sensing Centre |
| 25 | NSIL | NewSpace India Limited |
| 26 | POEM | PSLV Orbital Experimental Module |
| 27 | PSLV | Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle |
| 28 | RTRS | Rail Track Rocket Sled |
| 29 | SAC | Space Applications Centre |
| 30 | SaRC | Satellite Research Centre |
| 31 | SCL | Semi-Conductor Laboratory |
| 32 | SDSC | Satish Dhawan Space Centre |
| 33 | SHAPE | Spectro-polarimetry of Habitable Planet Earth |
| 34 | SHAR | Sriharikota |
| 35 | TERLS | Thumba Equatorial Rocket Launching Station |
| 36 | UNNATI | UNispace Nanosatellite Assembly & Training by ISRO |
| 37 | URSC | U R Rao Satellite Centre |
| 38 | VKS | Vikram-Suborbital |
| 39 | VSSC | Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre |
| Read More |
- Maths General Knowledge Question And Answer
- List of Programming Languages and Their Developers
- General Knowledge Of Europe (Multiple Choice Questions)
- Indian Army Interview Questions And Answers You Must Know













Saved as a favorite, I love your website!
Thank you so much for sharing this wonderful post with us.
A great post without any doubt.